System Development: 7 Powerful Steps to Master the Process
Ever wondered how complex software systems come to life? It all starts with system development—a structured journey from idea to execution that powers everything from mobile apps to enterprise platforms.
[ez-toc]
What Is System Development and Why It Matters

System development refers to the comprehensive process of designing, building, testing, deploying, and maintaining information systems that meet specific user or business needs. It’s not just about writing code; it’s a full lifecycle approach that blends technical precision with strategic planning. Whether you’re developing a customer relationship management (CRM) tool or an AI-powered analytics dashboard, system development ensures that the final product is functional, scalable, and secure.
The Evolution of System Development
System development has come a long way since the early days of computing. In the 1960s and 70s, developers used rigid, linear models like the Waterfall method, where each phase had to be completed before moving to the next. While effective for well-defined projects, this approach lacked flexibility.
As technology evolved and user demands became more dynamic, new methodologies emerged. The 1990s saw the rise of iterative models, and by the 2000s, Agile and DevOps revolutionized how teams approach system development. Today, system development is faster, more collaborative, and increasingly automated.
- 1960s–1980s: Waterfall dominated with sequential phases
- 1990s: Prototyping and iterative models gained traction
- 2000s–Present: Agile, Scrum, and DevOps became industry standards
Key Stakeholders in System Development
Successful system development involves multiple stakeholders, each playing a critical role. These include:
- Project Managers: Oversee timelines, budgets, and team coordination.
- Business Analysts: Translate business needs into technical requirements.
- Developers: Write and maintain the codebase.
- QA Engineers: Ensure the system is bug-free and performs well.
- End Users: Provide feedback and validate system usability.
Collaboration among these groups is essential for delivering a system that meets both technical and business objectives. According to the Project Management Institute (PMI), projects with strong stakeholder engagement are 2.5 times more likely to succeed.
“The best systems are not built in isolation—they emerge from continuous collaboration between technical teams and business stakeholders.” — Dr. Linda Rising, Software Development Expert
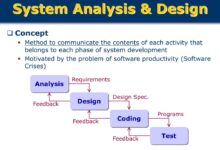
The 7 Phases of System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
The System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a proven framework used to design and implement high-quality information systems. It consists of seven distinct phases, each with specific goals and deliverables. Understanding these phases is crucial for managing risk, ensuring quality, and delivering value on time.
1. Requirement Analysis
This is the foundation of any system development project. During this phase, teams gather, analyze, and document the functional and non-functional requirements of the system. Techniques like interviews, surveys, and use case modeling help identify what the system should do.
Key activities include:
- Identifying user needs and pain points
- Defining system scope and objectives
- Documenting requirements in a Software Requirements Specification (SRS)
A poorly defined requirement can lead to scope creep, budget overruns, and project failure. According to a study by the Standish Group, over 40% of failed IT projects cite incomplete requirements as a primary cause.
2. System Design
Once requirements are clear, the next step is system design. This phase translates user needs into a technical blueprint. It includes both high-level architecture (how components interact) and low-level design (detailed module specifications).
Design outputs typically include:
- System architecture diagrams
- Data flow diagrams (DFDs)
- Database schema designs
- UI/UX wireframes
This phase ensures that developers have a clear roadmap before coding begins. Tools like UML (Unified Modeling Language) and platforms such as Lucidchart are commonly used to visualize system design.
3. Implementation (Coding)
This is where the actual system development takes place. Developers write code based on the design specifications, using programming languages and frameworks suited to the project. Whether it’s Python for backend logic or React for frontend interfaces, the implementation phase brings the system to life.
Best practices during implementation include:
- Following coding standards and style guides
- Using version control systems like Git
- Writing modular, reusable code
Continuous integration (CI) tools like Jenkins or GitHub Actions help automate testing and deployment, reducing human error and speeding up delivery.
4. Testing
No system development process is complete without rigorous testing. This phase ensures the system works as intended and is free from critical bugs. Testing can be manual or automated and includes various types:
- Unit Testing: Tests individual components or functions.
- Integration Testing: Checks how modules work together.
- System Testing: Validates the complete system against requirements.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): End users test the system in real-world scenarios.
Automated testing frameworks like Selenium, JUnit, and Cypress have made it easier to maintain code quality throughout the system development lifecycle.
5. Deployment
Once testing is successful, the system is ready for deployment. This phase involves installing the system in the production environment and making it available to users. Deployment strategies vary:
- Big Bang Deployment: The entire system goes live at once.
- Phased Deployment: Roll out features gradually.
- Blue-Green Deployment: Run two identical environments to minimize downtime.
Modern DevOps practices use CI/CD pipelines to automate deployment, ensuring faster and more reliable releases. Platforms like Docker and Kubernetes are widely used to containerize and orchestrate deployments.
6. Operation and Maintenance
After deployment, the system enters the operation phase. This is where it’s actively used by end users. However, system development doesn’t end here—maintenance is crucial for long-term success.
Maintenance activities include:
- Fixing bugs reported by users
- Applying security patches
- Optimizing performance
- Adding new features based on feedback
According to IBM, maintenance can account for up to 75% of the total cost of a software system over its lifetime. Proactive monitoring tools like Nagios and New Relic help teams detect and resolve issues before they impact users.
7. Evaluation and Feedback Loop
The final phase of SDLC is often overlooked but vital: evaluation. Teams assess the system’s performance, user satisfaction, and alignment with business goals. Feedback is collected and used to inform future iterations.
Key evaluation methods include:
- User surveys and interviews
- System performance metrics (uptime, response time)
- Return on Investment (ROI) analysis
This phase closes the loop and sets the stage for continuous improvement, especially in Agile environments where system development is an ongoing cycle.
Popular System Development Methodologies
Choosing the right methodology is critical to the success of any system development project. Different approaches suit different types of projects, team sizes, and organizational cultures. Let’s explore the most widely used methodologies today.
Waterfall Model
The Waterfall model is one of the oldest and most straightforward system development methodologies. It follows a linear, sequential approach where each phase must be completed before the next begins.
Advantages:
- Clear structure and documentation
- Easy to manage and track progress
- Suitable for projects with stable requirements
Disadvantages:
- Limited flexibility for changes
- Testing occurs late in the cycle
- High risk of failure if requirements are misunderstood
Despite its limitations, Waterfall is still used in industries like aerospace and healthcare, where regulatory compliance and documentation are paramount.
Agile Methodology
Agile is a game-changer in system development. It emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and customer feedback. Instead of delivering the entire system at once, Agile breaks the project into small, manageable increments called sprints—typically lasting 2–4 weeks.
Key principles of Agile include:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
Frameworks like Scrum and Kanban are popular implementations of Agile. According to the State of Agile Report, over 70% of organizations use Agile to improve delivery speed and adaptability.
“Agile is not just a methodology—it’s a mindset shift toward responsiveness and value-driven development.” — Ken Schwaber, Co-Creator of Scrum
DevOps Integration
DevOps is not a standalone methodology but a cultural and technical extension of Agile. It bridges the gap between development (Dev) and operations (Ops), enabling faster and more reliable system development and deployment.
Core DevOps practices include:
- Continuous Integration (CI)
- Continuous Delivery (CD)
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
- Automated monitoring and logging
Tools like Jenkins, Ansible, and Terraform empower teams to automate repetitive tasks, reduce errors, and accelerate time-to-market. Companies like Amazon and Netflix attribute their rapid innovation to strong DevOps practices.
Tools and Technologies in Modern System Development
Today’s system development landscape is powered by a vast ecosystem of tools and technologies. From integrated development environments (IDEs) to cloud platforms, these tools enhance productivity, collaboration, and scalability.
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs)
IDEs are software applications that provide comprehensive facilities for system development. They typically include a code editor, debugger, and build automation tools.
Popular IDEs include:
- Visual Studio Code: Lightweight, extensible, and supports multiple languages.
- IntelliJ IDEA: Preferred for Java and Kotlin development.
- Eclipse: Open-source IDE widely used in enterprise environments.
These tools streamline coding, reduce errors, and improve developer efficiency.
Version Control Systems
Version control is essential for managing code changes, especially in team environments. It allows developers to track modifications, collaborate without conflicts, and roll back to previous versions if needed.
The most widely used system is Git, hosted on platforms like:
These platforms also support issue tracking, code reviews, and CI/CD pipelines, making them central to modern system development workflows.
Cloud Platforms and Infrastructure
Cloud computing has transformed system development by providing on-demand access to computing resources. Instead of investing in physical servers, teams can deploy applications on cloud platforms with scalability and reliability.
Leading cloud providers include:
These platforms offer services like virtual machines, databases, AI tools, and serverless computing, enabling rapid prototyping and global deployment.
Challenges in System Development and How to Overcome Them
Despite advances in tools and methodologies, system development remains a complex endeavor. Teams often face challenges that can derail timelines, inflate budgets, or compromise quality. Recognizing these issues early is key to mitigation.
Scope Creep
Scope creep occurs when project requirements expand beyond the original plan without proper approval or resource adjustment. It’s one of the most common causes of project failure.
How to prevent it:
- Define clear project scope and objectives upfront
- Use change control processes to evaluate new requests
- Regularly communicate with stakeholders to align expectations
A study by PMI found that 52% of projects experience scope creep, often due to poor requirement management.
Poor Communication
Miscommunication between developers, analysts, and stakeholders can lead to misunderstandings, incorrect features, and rework.
Solutions include:
- Holding regular stand-up meetings (especially in Agile)
- Using collaboration tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or Jira
- Documenting decisions and sharing them across teams
Effective communication reduces ambiguity and keeps everyone aligned.
Security Vulnerabilities
With cyber threats on the rise, security must be integrated into every phase of system development. Many breaches occur due to unpatched vulnerabilities or insecure coding practices.
Best practices for secure system development:
- Adopt Secure Software Development Lifecycle (SSDLC)
- Conduct regular code reviews and penetration testing
- Use security-focused frameworks like OWASP
The OWASP Top 10 list highlights the most critical web application security risks, serving as a valuable guide for developers.
The Role of AI and Automation in System Development
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation are reshaping system development, making it faster, smarter, and more efficient. From code generation to testing, AI-powered tools are augmenting human capabilities.
AI-Powered Code Assistants
Tools like GitHub Copilot and Amazon CodeWhisperer use machine learning to suggest code snippets in real time. Trained on vast code repositories, these assistants help developers write code faster and with fewer errors.
Benefits include:
- Reduced coding time
- Improved code quality
- Learning aid for junior developers
However, developers must review AI-generated code for security and correctness, as it may introduce vulnerabilities.
Automated Testing and Debugging
AI is also transforming testing. Tools like Testim.io and Applitools use AI to create and maintain test cases, detect visual bugs, and predict failure points.
Advantages:
- Faster test execution
- Higher test coverage
- Reduced manual effort
Automation allows QA teams to focus on complex scenarios while routine checks are handled by AI.
Predictive Analytics for Project Management
AI can analyze historical project data to predict risks, estimate timelines, and optimize resource allocation. Tools like Forecast and ClickUp use AI to provide real-time insights into project health.
This predictive capability helps managers make data-driven decisions and avoid common pitfalls in system development.
Future Trends in System Development
The future of system development is exciting, driven by innovation in AI, cloud computing, and low-code platforms. Staying ahead of these trends is essential for organizations aiming to remain competitive.
Rise of Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
Low-code and no-code platforms like OutSystems, Mendix, and Bubble are democratizing system development. They allow non-technical users to build applications using drag-and-drop interfaces.
Impact:
- Accelerated development cycles
- Reduced dependency on IT teams
- Empowerment of citizen developers
According to Gartner, by 2025, 70% of new applications will use low-code or no-code technologies.
Serverless Architecture
Serverless computing allows developers to build and run applications without managing servers. Providers like AWS Lambda and Azure Functions handle infrastructure automatically.
Benefits:
- Lower operational costs
- Automatic scaling
- Focus on business logic rather than infrastructure
This trend is making system development more agile and cost-effective.
Sustainable Software Development
As environmental concerns grow, the tech industry is embracing sustainable practices. Green coding—writing energy-efficient software—is gaining traction.
Strategies include:
- Optimizing algorithms for lower CPU usage
- Reducing data transfer and storage
- Using energy-efficient cloud regions
Organizations are beginning to measure the carbon footprint of their software, aligning system development with broader ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals.
What is the main goal of system development?
The main goal of system development is to create reliable, efficient, and user-friendly information systems that meet specific business or user requirements while adhering to budget, timeline, and quality standards.
What are the 7 phases of system development?
The 7 phases are: 1) Requirement Analysis, 2) System Design, 3) Implementation, 4) Testing, 5) Deployment, 6) Operation and Maintenance, and 7) Evaluation and Feedback Loop.
Which methodology is best for system development?
The best methodology depends on the project. Agile is ideal for dynamic, user-focused projects, while Waterfall suits well-defined, regulated environments. DevOps enhances both by improving deployment speed and reliability.
How does AI impact system development?
AI enhances system development through code assistance, automated testing, predictive analytics, and intelligent debugging, significantly improving speed, accuracy, and efficiency.
What tools are essential for modern system development?
Essential tools include IDEs (e.g., VS Code), version control (e.g., GitHub), CI/CD platforms (e.g., Jenkins), cloud services (e.g., AWS), and collaboration tools (e.g., Jira).
System development is a dynamic and multifaceted discipline that lies at the heart of digital transformation. From defining requirements to maintaining live systems, each phase plays a crucial role in delivering value. With the right methodologies, tools, and mindset—especially embracing Agile, DevOps, and AI—teams can build systems that are not only functional but future-ready. As technology evolves, so too must our approach to system development, ensuring innovation, security, and sustainability go hand in hand.
Further Reading: